REST API testing
Testing REST APIs is essential, and among all the tools available for API testing, REST Assured stands out for its features and effectiveness. This article will cover what REST Assured is and how it can be used for API test automation. We will also explore some sample requests and how REST Assured differs from Postman.
Table of contents
- What is REST Assured?
- What are Restful APIs?
- Request types in REST API
- How REST Assured can be used for API test automation
- Sample request and response in REST Assured
- Common error messages in REST Assured
- REST Assured vs Postman
- Conclusion
What is REST Assured?
REST Assured is an open-source Java-based library for API (Application Programming Interface) test automation, popularly used to test RESTful APIs. It helps users validate different modes of RESTful services, such as handling request payloads and verifying response status codes and contents. It also helps users send HTTP requests to RESTful endpoints and verify the responses received. It provides a domain-specific language (DSL) that aligns with the structure of HTTP requests and responses.
The REST Assured library has been developed and maintained by Johan Haleby with the assistance of several other contributors over the years. Johan initiated this project while he was employed at Jayway in December 2010.
What are Restful APIs?
A RESTful API, which stands for Representational State Transfer API, is a type of API that follows the principles of REST architecture and also allows communication with RESTful web services. These APIs help clients interact with server-side resources using standard HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, and PATCH. REST APIs typically communicate using lightweight data formats such as JSON or XML, making them widely compatible with various programming languages and platforms compared to SOAP.
Request types in REST API
In REST-based Architecture, HTTP commonly uses five methods: POST, GET, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE. These correspond to the four basic operations in a database: create, read, update, and delete. Less frequently used methods include OPTIONS and HEAD.
GET
The GET method is used to retrieve information from a server. For example, when you visit a webpage URL, your browser sends a GET request to the server to fetch the page. It responds with a status code 200 and the requested data if everything’s okay. In case of an error, it returns a 404 (NOT FOUND) or 400 (BAD REQUEST) response code.
POST
A POST request sends data to the server to create a new resource. It’s like filling out a form online and submitting it. After successful creation, the server responds with a status code 201 and a link to the newly created resource.
PUT
PUT is used to update an existing resource. The user sends the updated data to the server, and if the update is successful, the server responds with a status code of 200 or 204. PUT can also create a resource if it doesn’t exist, but this is less common.
PATCH
PATCH is similar to PUT, but instead of sending the entire updated resource, you only send the changes part. It’s like editing a document instead of rewriting the whole thing. PATCH is used when you don’t want to send the entire resource back and forth.
DELETE
It’s used to delete a resource from the server. After successful deletion, the server responds with a status code of 200.
How REST Assured can be used for API test automation
Setup
Set up your testing environment by adding REST Assured to your project dependencies. You can do this using a build automation tool like Maven or Gradle. For example, in a Maven project, you would include REST Assured as a dependency in your pom.xml file.
<dependency>
<groupId>io.rest-assured</groupId>
<artifactId>rest-assured</artifactId>
<version>4.4.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Writing tests
Write tests and specify the HTTP request method, such as GET or POST, headers, parameters, request body, and expected response. These tests can be written in any IDE, like IntelliJ IDEA, or within a Selenium framework.
Sending requests
Once you’ve written your test cases, send HTTP requests to your API endpoints. REST Assured handles the low-level details of sending requests over the network.
Validating responses
After sending a request, REST Assured captures the response from the server, allowing you to perform assertions to validate the response. You can verify the status code, response body, and response headers to ensure your API behaves as expected.
Automation
REST Assured integrates easily with popular testing frameworks like JUnit and TestNG, allowing you to automate the execution of your API tests. You can integrate your tests into your CI pipeline to prevent code regressions.
Sample request and response in REST Assured
The following code snippets use REST Assured within a TestNG and Selenium Java project to showcase how API requests and responses are handled.
Page class
Let’s create the method that will be used to make the API request:

Every API request will have, at a minimum, query parameters and the type of request being made, such as GET. The example above uses a page query parameter and a GET request.
Test class
Let’s create the test method:

Request
In our test scenario, we used REST Assured to send a GET request to the /api/users endpoint with a page parameter value of 2. The request was initiated using the ApiClient class that handles API requests:
Response response = ApiClient.getUsers(2);Within this request:
- The base URI for the API is set to
https://reqres.in. - A
GETrequest is directed to the/api/usersendpoint, with a query parameterpageset to2.
Response
After sending the request, REST Assured captures the server’s response. Here’s a glimpse at the received response in the console output:
Response status line: HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Sample Request: GET /api/users?page=2
Sample Response: {"page":2,"per_page":6,"total":12,"total_pages":2,"data":[{"id":7,"email":"michael.lawson@reqres.in","first_name":"Michael","last_name":"Lawson","avatar":"https://reqres.in/img/faces/7-image.jpg"},{"id":8,"email":"lindsay.ferguson@reqres.in","first_name":"Lindsay","last_name":"Ferguson","avatar":"https://reqres.in/img/faces/8-image.jpg"},{"id":9,"email":"tobias.funke@reqres.in","first_name":"Tobias","last_name":"Funke","avatar":"https://reqres.in/img/faces/9-image.jpg"},{"id":10,"email":"byron.fields@reqres.in","first_name":"Byron","last_name":"Fields","avatar":"https://reqres.in/img/faces/10-image.jpg"},{"id":11,"email":"george.edwards@reqres.in","first_name":"George","last_name":"Edwards","avatar":"https://reqres.in/img/faces/11-image.jpg"},{"id":12,"email":"rachel.howell@reqres.in","first_name":"Rachel","last_name":"Howell","avatar":"https://reqres.in/img/faces/12-image.jpg"}],"support":{"url":"https://reqres.in/#support-heading","text":"To keep ReqRes free, contributions towards server costs are appreciated!"}}
PASSED: myproject.tests.ApiTest.testGetUsers
===============================================
Default test
Tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Skips: 0Code language: PHP (php)This response provides:
- A response status code 200 (SUCCESS)
- The body of the response with details about the current page, number of users per page and total pages.
- User information such as ID, email, first name, last name, and avatar.
Common error messages in REST Assured
NullPointerException error
This error occurs because the RestAssured.get() method fails to fetch a valid response from the specified URL. As a result, the response object becomes null, leading to a NullPointerException when attempting to invoke methods on it, such as getStatusCode(). This could happen for various reasons, including an incorrect URL, server unavailability, or issues with network connectivity.

To fix this issue, the user must ensure that the RestAssured.get() request is successful and returns a valid response. Double-check the request URL and ensure the API endpoint is accessible and returns data as expected.
UnknownHostException error
The UnknownHostException error typically occurs when Java tries to resolve a hostname into an IP address but fails to find the hostname’s corresponding IP address. This can happen for various reasons, such as DNS misconfiguration, network connectivity issues, or incorrect hostname resolution settings.

To solve this issue, verify the hostname or URL used in your API request. Check that the spelling of the hostname is correct and that it points to a valid endpoint. Also, check your network settings and DNS configuration to ensure the hostname can be resolved to an IP address.
JSONParser error
The JSONParser issue typically occurs due to missing or incorrect dependencies in the test environment. This error occurs when the compiler cannot recognize or resolve certain types, such as JSONParser or ParseException, which are essential for parsing JSON data.

To fix the JsonParser error, ensure that the required JSON parsing dependencies are properly configured. Verify that appropriate libraries are added to the build path or listed in the project’s dependencies. Include necessary import statements in the test class. You can resolve the error by addressing these issues and executing the test successfully.
RequestSpecification error
This error occurs when there is a mismatch between the package declaration in the Java source file and the actual directory structure of the file system. When TestNG attempts to instantiate a test class, it expects the package declaration to match the directory structure where the class file resides. If there is a mismatch, TestNG cannot locate the class file and fails to instantiate the class.
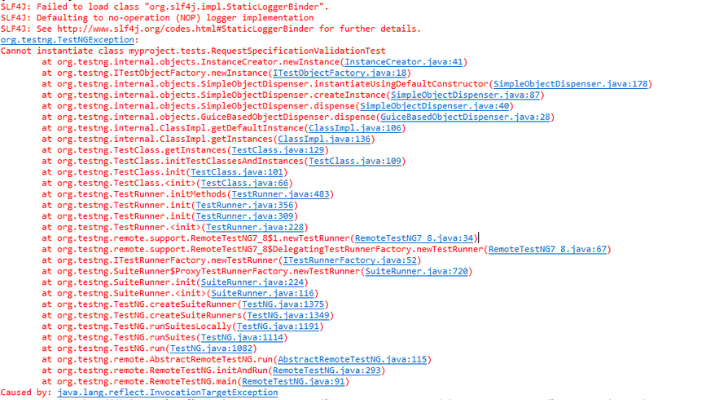
To fix this issue, the user must ensure that the package declaration in the Java source file matches the system’s directory structure. They should verify that the Java file is in the correct directory corresponding to its package declaration.
REST Assured vs Postman

REST Assured and Postman are useful tools during the testing process of APIs, but each has different features. Postman is a multifunctional tool performing exploratory, manual, and automation testing. It has both open-source and advanced versions, while REST Assured is only designed for automated API testing using Java and is entirely open-source.
Postman primarily supports JavaScript scripting, while REST Assured supports multiple languages. Moreover, Postman generally offers faster API response times, but REST Assured is better regarding code reusability.
REST Assured provides more scope for integration with other tools and frameworks, allows customized reports, and allows parallel execution. Conversely, Postman has limited integration capabilities and supports only one data file per collection.
Final thoughts on mastering REST Assured API testing
In conclusion, Rest Assured is a powerful framework for automating API tests with an insightful DSL and seamless integration with popular testing frameworks. By following these contents and utilizing Rest Assured’s capabilities, every professional can ensure the stability of their APIs and simplify their testing processes.
Related articles
- HTTP Request Methods & API Testing
- SOAP vs. REST: How to choose
- Automating API Testing with Postman
- Hamcrest Matchers
- Insomnia API testing
Follow our blog
Be the first to know when we publish new content.
What is REST Assured API testing?
- How to find an element in Selenium - October 5, 2024
- Resolved: SessionNotCreatedException - October 2, 2024
- Katalon Recorder Automation Overview - September 12, 2024
